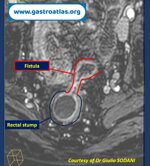
#lorem ipsum#
Via San Esempio 201, 219038
+ 39 378162183612387612
I am aware that you will use these images for your presentations and I accept it, I would do the same.
At least thank the author of the report and the website
(example: courtesy of AUTHOR(S), see more on www.gastroatlas.org)
Sort by technique (Endoscopy, Ultrasound, etc.) or anathomical site
Free search text (e.g. by author, pathology, anathomical site, etc.)
In Stock




In Stock

In Stock


In Stock
In Stock
1 2 3 4 › 4
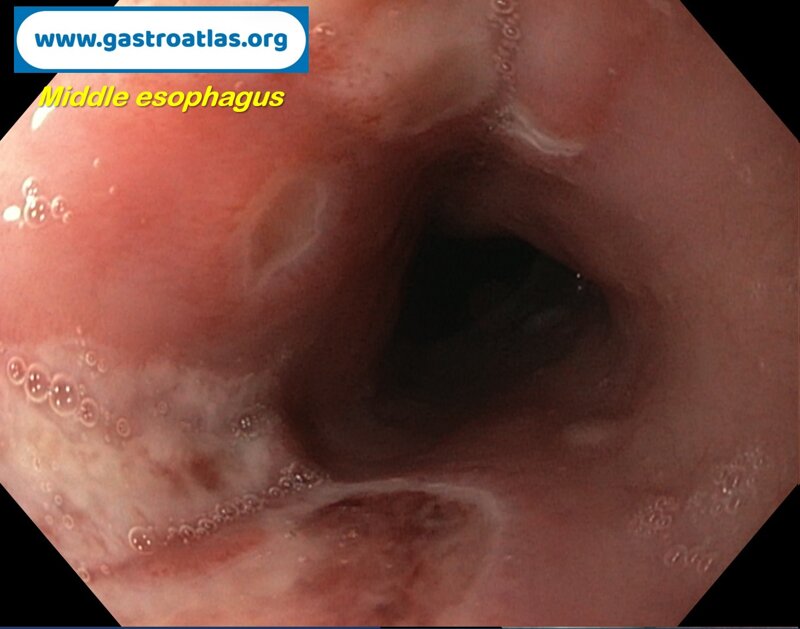
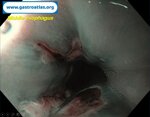
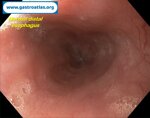
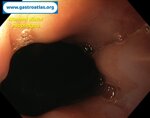
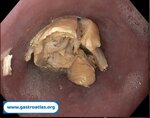
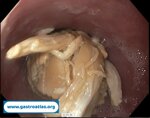
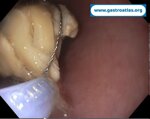
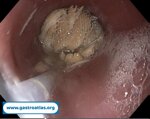
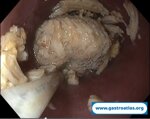
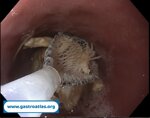
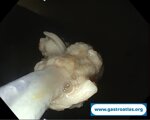
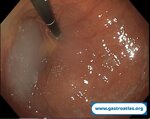
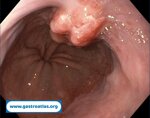
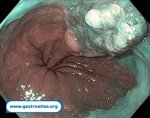
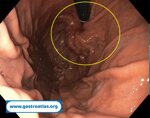
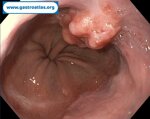
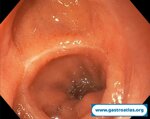
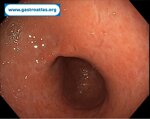
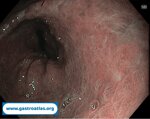
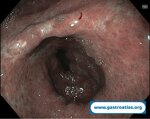
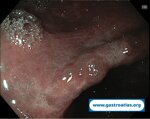
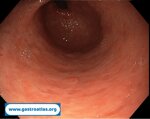
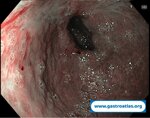
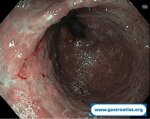
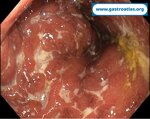
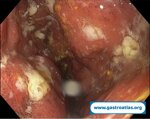
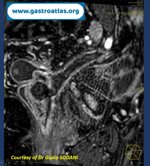
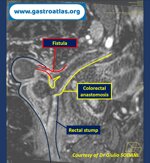
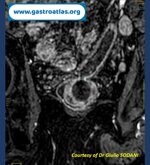
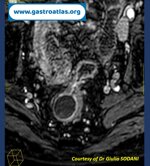
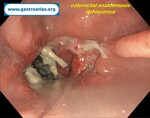
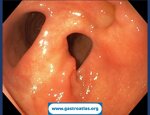
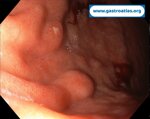
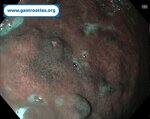
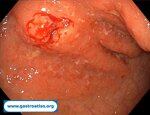
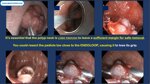
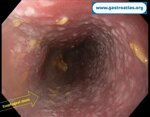
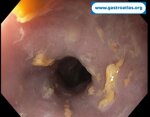
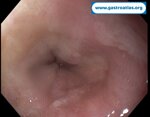
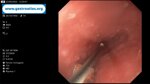
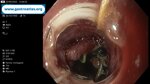
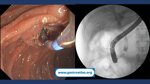
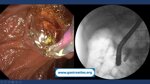
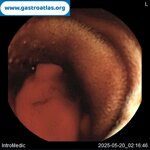
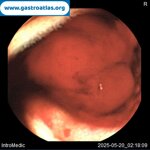
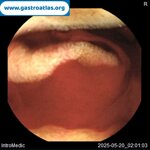
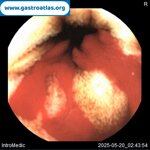
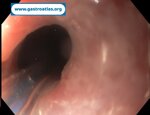
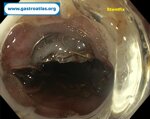
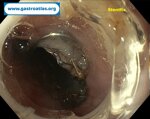
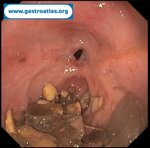
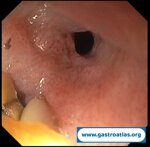
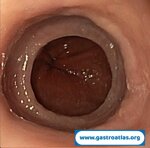
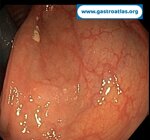
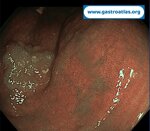
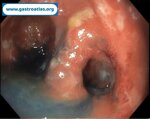
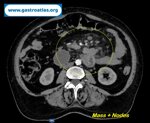
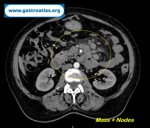
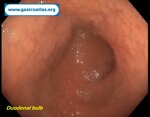
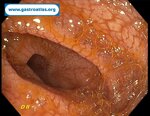
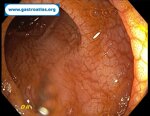
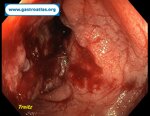
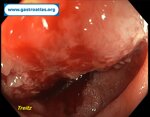
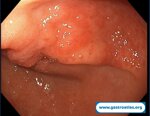
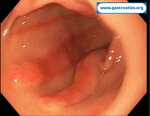
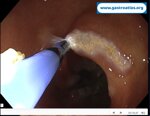
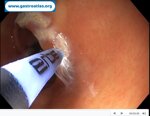
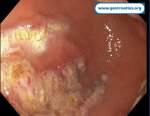
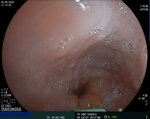
Pill‑induced esophagitis (drug‑induced esophagitis)
2 Endoscopy 1 Clinical case B Esophagus dysphagia, odynophagia, pill‑induced esophagitis, drug‑induced esophagitis, antibiotics, doxycycline, nsaids, bisphosphonates, potassium chloride
In Stock
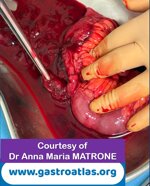
Author: SCANNI Stefania, Roma Italy
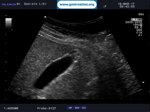
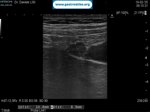
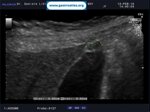
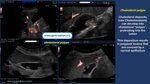
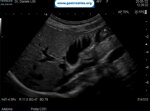
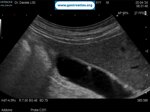
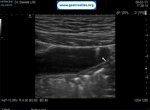
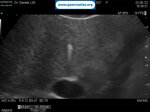
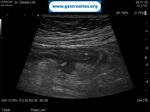
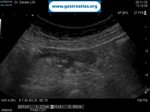
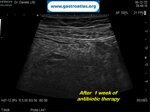
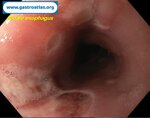
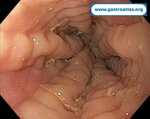
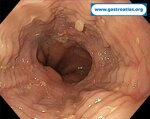
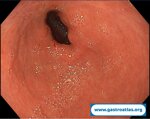
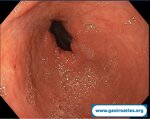
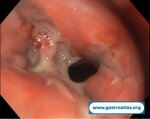
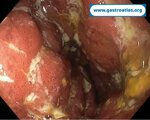
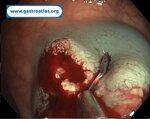
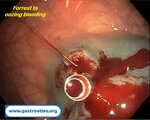
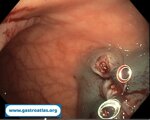
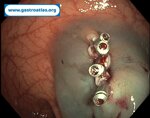
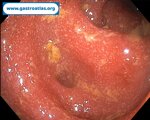
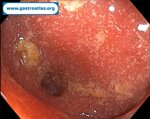
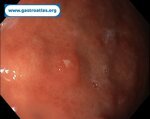
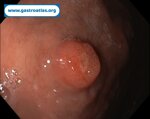
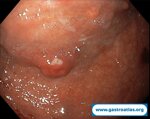
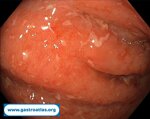
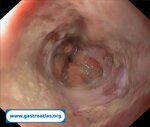
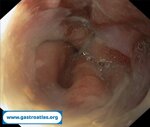
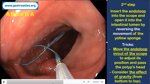
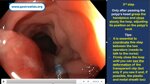
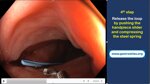
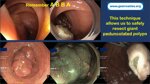
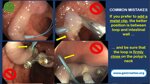
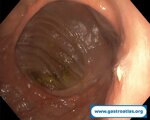
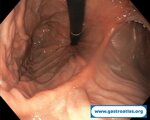
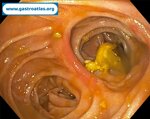
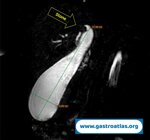
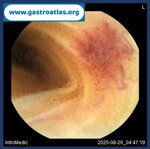
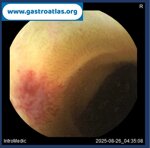
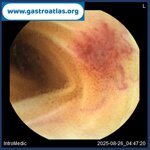
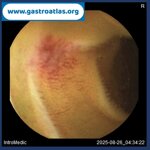
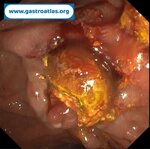
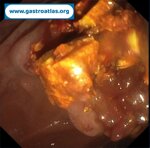
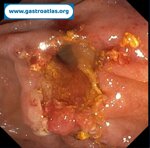
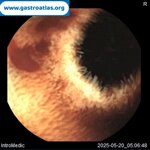
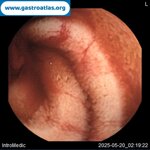
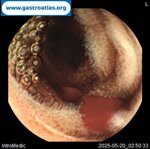
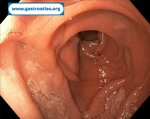
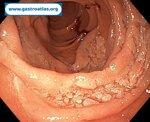
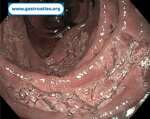
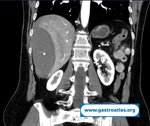
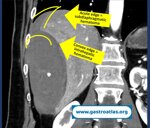
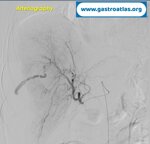
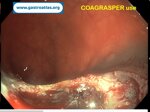
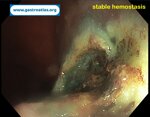
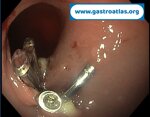
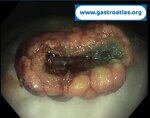
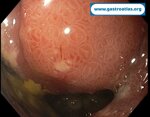
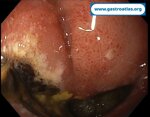
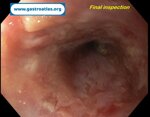
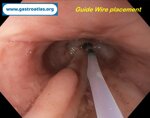
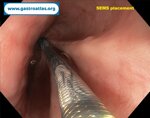
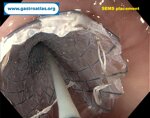
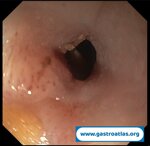
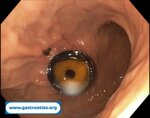
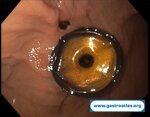
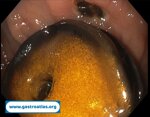
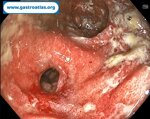
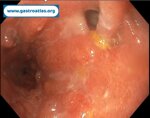
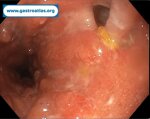
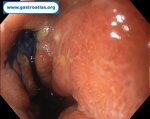
Pill‑induced esophagitis (drug‑induced esophagitis) is an acute injury of the esophageal mucosa caused by medications that lodge and dissolve in the esophagus, producing local caustic damage. It typically presents with sudden retrosternal pain, odynophagia, and dysphagia.
It occurs when a medication remains in contact with the esophageal lining, releasing acidic, alkaline, or hyperosmolar contents that injure the mucosa.
High‑risk drug classes are: Antibiotics (Doxycycline, tetracycline, clindamycin), NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, naproxen), Bisphosphonates (Alendronate), Potassium chloride (KCl tablets)
In this case the patient intaked Doxycycline